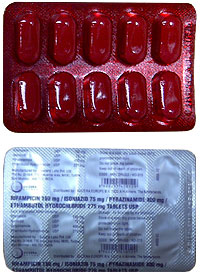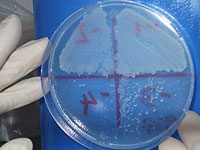
Impact
Mankind has been confronted with TB since ancient times. Modern strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis seem to have originated from a common ancestor about 15,000-20,000 years ago. Archeological evidence of early TB has been found in for example Egyptian and Peruvian mummies, and was already described in classical Greece as phthisis. In 19th century Western Europe,…